Chemosis Eye Irritation: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
Home / Eye Conditions & Eye Diseases /
Last Updated:
Table of Contents
Chemosis presents a host of symptoms that range from mild discomfort to more severe complications. As a common condition, it can stem from a variety of causes such as allergies, infections, trauma, or eye surgeries.
What Is Chemosis?
Chemosis, or conjunctival chemosis, is swelling of the eye’s conjunctiva (the outer layer of the eye). This can result in the eye appearing puffy, red, and irritated
Causes of chemosis range from allergies and infection to trauma and eye surgery. Symptoms include itchiness, discomfort, swelling, and discharge from the eye.
You deserve clear vision. We can help.
With 135+ locations and over 2.5 million procedures performed, our board-certified eye surgeons deliver results you can trust. Your journey to better vision starts here.
Treatment for chemosis will vary according to the particular cause. Treatments include antibiotics, antihistamines, other eye drops, and surgery (in extreme cases). Home remedies, such as applying cold compresses, are also recommended.
Signs & Symptoms of Chemosis
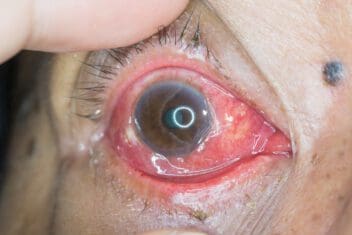
Due to the swelling, Chemosis can sometimes look like a blister on the eye. The eye may water, and the discharge may appear yellowish. The swelling can get significant, even leading to difficulty closing the eye.
The eye may feel itchy, uncomfortable, and generally irritated. Due to the swelling and watering, vision can be blurred or doubled.
Causes of Chemosis in the Eye
The most common cause of chemosis is simply irritation of the eye. Some irritant came in contact with the eye and triggered the swelling.
This irritation can be due to several causes, such as these:
- Animal dander
- Pollen
- Dust
- Other allergens
- Rubbing your eyes
- Infection
- Steroid use
- Trauma to the eye
- Eye surgery
Thyroid eye disease can also cause chemosis. This eye disease is generally associated with Graves’ disease, an autoimmune disorder in which the body attacks itself, leading to various eye issues. Chemosis is very common in those with thyroid eye disease, so ophthalmologists will monitor patients to detect its presence as early as possible.
Angioedema of the eyes is another cause of chemosis. This is simply an allergic reaction around the eye area. Any allergen can cause this to occur.
How Is Chemosis Diagnosed?
Chemosis is diagnosed through a series of steps by an ophthalmologist. Initially, the patient’s history is evaluated, including the onset of symptoms, potential exposure to allergens or irritants, and any recent eye trauma or systemic illnesses. The doctor then performs a physical examination, assessing the eyes for any signs of inflammation or swelling, often using a slit lamp to view the eye structures in detail.
Chemosis Treatment: Home Remedies & In-Office Care
Primary treatments for chemosis involve home remedies to reduce inflammation and in-office care to address the underlying cause.
Home Remedies to Reduce Swelling
To reduce swelling at home, try these tips:
- Apply a cool compress to the eye. This can help to reduce inflammation and soothe the eye area.
- Avoid contact lenses. Wear glasses while the eye is swollen.
- Do not wear eye makeup.
- Sleep with your head elevated. This can help to lessen swelling.
In-Office Care for Chemosis
Your doctor will attempt to identify the underlying cause of chemosis. Treatment will vary depending on that cause:
| Cause of Chemosis | In-Office Care |
|---|---|
| Allergies | Prescription of antihistamines or other allergy medications; over-the-counter allergy medication might be recommended. |
| Bacterial Infection | Prescription of antibiotics, potentially as eye drops, topical ointments, or oral medication. |
| Viral Infection | Recommendation of regular cold compresses and lubricating eye drops to alleviate discomfort, as direct medication often isn’t available. |
| Trauma | Assessment of the injury’s extent with subsequent recommendations for treatment based on its severity. |
| Severe Cases | Potential need for surgery to drain fluid from the area, although this is rare. |
You deserve clear vision. We can help.
With 135+ locations and over 2.5 million procedures performed, our board-certified eye surgeons deliver results you can trust. Your journey to better vision starts here.
When to See a Doctor
If you experience substantial swelling, see a doctor promptly. You’ll also want to see a doctor if you experience changes in your vision, pain in your eye, or any breathing changes. If you are unable to fully close your eye, you need medical attention.
How Long Does Chemosis Last?
Chemosis duration can vary significantly depending on the underlying cause. If it’s related to an allergic reaction or minor irritant, chemosis might resolve within a few hours to a couple of days once exposure is eliminated and over-the-counter antihistamines or eye drops are used.
Post-surgical chemosis usually improves within a week, but it can occasionally last longer. Chemosis related to more serious conditions, such as infections or systemic diseases, may persist until the underlying condition is properly treated.
Regardless of the cause, any persistent or recurring chemosis should be evaluated by a healthcare professional to identify and treat any potential underlying conditions. Always consult with an ophthalmologist if chemosis doesn’t improve promptly or is accompanied by pain, vision changes, or severe discomfort.
How to Prevent Chemosis
If chemosis is related to allergies, keeping your allergies under control is the best prevention method. This often involves regularly taking antihistamines.
Infection-related chemosis can be prevented with a comprehensive hygiene routine.
- Don’t touch your eyes without first washing your hands.
- Never share makeup or other products that touch your eyes with anyone else.
- Replace eye makeup as recommended since these products can carry bacteria over time.
- Don’t wear contacts for longer than recommended.
Chemosis FAQs
Is chemosis serious?
Most of the time, chemosis is relatively easy to treat. In severe cases, a surgical procedure may be required, but in most cases, chemosis is not serious.
How long does chemosis last?
Mild chemosis generally goes away within a couple days, but it can last weeks or even months. Very rare cases can last up to a year. See a doctor if the swelling does not clear within a few days.
Is chemosis an emergency?
If you experience an allergic reaction, it can be an emergency. Call a doctor promptly if you experience breathing issues, severe pain or irritation, or substantial swelling.
In most cases, chemosis will clear within a few days, but it’s wise to see a doctor early in case there is a complication or more serious underlying issue.
You deserve clear vision. We can help.
With 135+ locations and over 2.5 million procedures performed, our board-certified eye surgeons deliver results you can trust. Your journey to better vision starts here.
References
- Chemosis. (June 2021). Mount Sinai.
- Orbital Inflammatory Disease: Pictorial Review and Differential Diagnosis. (April 2014). World Journal of Radiology.
- How to Recognize & Treat Thyroid Eye Disease. (November 2013). Review of Ophthalmology.
- Ocular Angioedema. American Academy of Optometry.
- A Contemporary Look at Allergic Conjunctivitis. (January 2020). Allergy, Asthma & Clinical Immunology.
- Conjunctival Chemosis: A Case Series of Systemic Causes. Canadian Journal of Ophthalmology.
This content is for informational purposes only. It may have been reviewed by a licensed physician, but is not intended to serve as a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult your healthcare provider with any health concerns. For more, read our Privacy Policy and Editorial Policy.