Botox Around the Eyes: Expectations & Safety
Home / Vision Education Center /
Last Updated:
When most people think of Botox, they think about cosmetic injections, but this popular medical treatment is used to treat several more serious conditions.
Table of Contents
Ophthalmologists use Botox injections around or under the eyes to treat various conditions that impact vision. These include lazy eye, eyelid twitching, migraines, drooping eyelids, and excessive tearing or dry eyes.
There are some risks and side effects of Botox around the eyes that are important to understand. For the most part, Botox injections are safe solutions to symptoms of certain medical conditions.
What is Botox?
Botox is the brand name for a type of drug used to treat specific medical conditions or to improve the appearance of facial wrinkles. It’s a neurotoxin, or poison that changes the way the nervous system works.
The drug is prepared in the lab from a microbe. While the toxin is potentially deadly, it’s relatively safe to use in small doses for medical or cosmetic purposes.
You deserve clear vision. We can help.
With 135+ locations and over 2.5 million procedures performed, our board-certified eye surgeons deliver results you can trust. Your journey to better vision starts here.
Over the past 20 years, Botox’s popularity in American culture has grown as plastic surgery has become more widely accepted. It is injectable, relatively painless and affordable. Those who embrace it as an inexpensive way to look younger receive periodic injections to get rid of wrinkles around the lips, eyes, eyebrows and forehead.
How Does Botox Work
A plastic surgeon injects a prescribed Botox dose into the muscles around your eye lines. The toxin temporarily paralyzes the muscles, rendering them unable to receive nerve signals that normally cause them to contract.
Facial wrinkles disappear, and the treated area appears smooth until the drug’s effect wears off. For eye lines, the effects last about three to four months after injections.
Cosmetic Uses for Botox Around the Eyes
Botox is approved for cosmetic uses around the eyes. It can improve the appearance of facial lines, such as:
- Glabellar lines
- Crow’s feet
- Forehead lines
Glabellar Lines
These wrinkles usually appear between your eyebrows over the forehead, giving you an older look. A Botox injection weakens your glabellar muscles, eliminating the lines to create a smoother facial appearance.
Crow’s Feet
Also called lateral canthal lines, crow’s feet forms around the corners of your eyes. Botox can eliminate these facial wrinkles for several months.
Forehead Lines
Botox can also fix horizontal forehead lines above your eyes. The drug eliminates the wrinkling by inhibiting the function of your forehead muscles.
Consult your plastic surgeon about Botox for cosmetic use if you have moderate or severe eye lines. However, you need a different type of neurotoxin injection for eye problems like lazy eye or eye twitching.
Is Botox Used for More Than Just Cosmetic Reasons?
There are two major types of Botox. One is for cosmetic treatments. The second treats certain health disorders. They two products differ slightly in potency and are not interchangeable. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Botox therapy for the following conditions:
- Overactive bladder in adults: This condition causes issues like unintentional passage of urine or frequent urination.
- Neurogenic detrusor overactivity (NDO) in children: This is a type of bladder dysfunction that affects children with a brain or central nervous system disorder. Botox is approved to treat the condition in minors who are at least 5 years old.
- Chronic migraine: Your doctor may recommend Botox treatment if you experience a migraine for 15 days or more per month and if each episode lasts for four or longer.
- Painful, stiff muscles (spasticity): This condition can affect different muscles throughout your body, inhibiting functions like speech or movement. A Botox injection can relax the muscles, restore lost body functions and ease pain.
- Cervical dystonia: This is the involuntary contraction of neck muscles. It can cause your head to twist awkwardly, often with significant pain.
- Hyperhidrosis: People with this disease tend to sweat excessively without an apparent cause.
- Blepharospasm: This when your eyes twitch involuntarily. A Botox injection can treat the condition by relaxing the muscles that control your eyelids.
- Crossed eyes (strabismus): Botox can be used to relax muscles that control eye movement to treat this disorder.
Vision Procedures Around the Eye Using Botox

While many people may have some Botox injections in middle age or later to reduce the number of wrinkles around their eyes, eyebrows, and forehead, using Botox injections in, around, and under the eye can treat specific medical conditions. These conditions include:
Strabismus (lazy eye)
This condition is essentially an imbalance in strength in the muscles that keep the eyes focused and moving together. Strabismus can also be caused by nerve damage around the eyeball or leading from the eye to the brain, so visual signals from one eye are not interpreted as well as from the other eye.
Strabismus is more common in children, and it usually involves placing an eye patch over the dominant eye, so the less muscle-toned eye can gain strength, both in muscle coordination and the optic nerve’s signals to the brain. Eye glasses and surgery can also help to correct lazy eye, but they are not needed as often as simple early childhood training.
Symptoms of strabismus, if it is not obvious, include:
- Impaired vision, particularly in one eye more than the other.
- Double vision.
- Lower depth perception.
- Eye strain.
Adults with strabismus that begins suddenly may have an underlying condition that requires medical treatment. Lazy eye by itself, though, is very treatable
Botox injections are typically one of the last approaches to managing the condition. Eye exercises along with corrective lenses via glasses or contacts are the main approach to treatment.
Blepharospasm (eye twitching)
Sometimes, muscles around the eye near the eyelid can twitch involuntarily. This is called myokymia, and it can involve the lower lid, upper lid, or both.
For most people, these twitches are mild, and they feel like a quick tug. Most people experience them once in a while; however, for some, they become chronic and can impact vision by forcing both eyelids closed completely. These episodes may occur on and off for several days and then go away for months. Their unpredictability can make them disruptive. When this becomes excessive, Botox injections can relieve that twitching.
In rare cases, blepharospasm can be an early symptom of a chronic movement disorder, especially when facial spasms become larger and are accompanied by other movements. Stress, exhaustion, eye or eyelid strain, eye irritation, medication side effects, or recreational substances like tobacco and alcohol can all contribute to this condition’s severity.
Additionally, blepharospasm may be made worse by:
- Blepharitis (inflammation of the eyelid).
- Conjunctivitis (pink eye).
- Dry eyes.
- Light sensitivity.
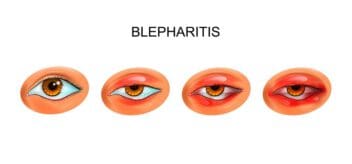
If blepharospasm is coupled with redness, swelling, discharge, upper eyelid drooping, several weeks of twitching almost nonstop, full closing of both eyes that you cannot control, and twitching spreading to other parts of your face, it is time to see a doctor.
There are several approaches to treatment, including lifestyle changes, better sleep, over-the-counter eye drops, and warm eye compresses. If the twitching continues while the main cause of blepharospasm is being treated, you may also get Botox injections.
Migraine
People who struggle with chronic migraine headaches report having trouble with light sensitivity, seeing flashes of light, or eye pain. If you experience migraine headaches for 15 days or more per month, Botox can help to alleviate those symptoms.
Drooping eyelid
In extreme cases, drooping in the eyelids from slack muscles or tendons can reduce one’s field of vision.
Eye dryness or excessive tearing
If there are blocks or excesses in the lacrimal flow, or watering of the eyes through the tear ducts, then Botox injections can help to manage this condition. The treatment can widen the area so blockages can move out or tears can move around them. Too much tearing and a Botox injection can help to tone the tear ducts, so they do not water so much.
You deserve clear vision. We can help.
With 135+ locations and over 2.5 million procedures performed, our board-certified eye surgeons deliver results you can trust. Your journey to better vision starts here.
Side Effects of Botox Around the Eyes
Both approved and unapproved use of Botox can have severe outcomes, some of which are life-threatening. See your doctor if you experience any complications after receiving a neurotoxin injection, including for cosmetic reasons.
Possible side effects of Botox around the eyes include:
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing, which can be fatal
- The traveling of the poison from the injection site to other parts of the body, causing severe complications
- Shortness of breath
- Anaphylaxis, a life-threatening allergic reaction with symptoms like nausea, breathing problems and shock
- Potentially fatal heart problems like irregular heart rate or heart attack
- Vision problems involving the cornea (the outermost layer at the front of the eye) after Botox treatment for twitching
- Dry eye, unusual sensitivity to light and other visual changes after cosmetic Botox use
- Double vision
Botox recipients also run a slight risk of viral disease transmission because the drug contains a human blood extract (proper donor blood screening should minimize this risk).
In some patients with unmanageable, life-threatening allergic reactions or immune responses to Botox, this therapy must be discontinued.
How Long Does Botox Around the Eyes Last?

For most people, Botox injections last between three and four months. Then, the effects will gradually start to wear off.
A medical study examining the effects of Botox specifically for crow’s feet around the eyes found that the median time the treatments lasted was between 119 and 121 days, which is about four months total. This timeline may be slightly different for you, depending on:
- Your overall health.
- Your age.
- How much time you spend outdoors, especially without sunscreen.
- Genetic or family history.
- Your body’s reaction to Botox.
You can help Botox treatments last longer by avoiding direct sunlight as much as possible. Wear sunscreen for outdoor activities like swimming, running, and cycling. You should also wear sunglasses that provide protection against ultraviolet (UV) light, specifically sunglasses rated for UVA and UVB protection. If you cannot find these at a local retailer, you can ask your optometrist for recommendations.
Take care of the skin around your eyes with high-quality skincare products, and keep stress levels low. Not only will this help the Botox around your eyes to last as long as possible, but it will ensure healthier skin all over your body.
Costs
You can expect to pay $450 for a full dose of Botox. This is the cost you’ll incur each time you repeat the treatment/procedure. But the price can vary, based on several factors:
- Where you live
- Severity of your eye lines, which determines amount of Botox used
- Your plastic surgeon’s expertise
- Effort/skill required to repair your facial wrinkles
Alternatives
Besides Botox, numerous approved remedies exist for forehead lines, eye lines or similar facial wrinkles around the eyes. Common Botox alternatives include:
- Other neurotoxins
- Dermal fillers
- Hyaluronic acids
- Calcium hydroxylapatite (CaHA) microspheres
- Fat implants
Other neurotoxins
Products like Dysport, Xeomin and Jeuveau work the same way as Botox. An injection with any of these remedies weakens facial muscles responsible for lines around your eyes.
Dermal fillers
These injectables add tissue around deeply creased or folded facial areas to replace lost volume. They aren’t true Botox alternatives because they solve different types of facial appearance issues and don’t work by halting muscle function.
Hyaluronic Acids
Hyaluronic acid injections can restore your smooth facial appearance. The fillers replace hyaluronic acid that is lost in your body due to aging. Examples of these fillers are Juvederm and Restylane.
Calcium Hydroxylapatite (CaHA) Microspheres
This denser, firmer filler can be administered to augment various facial features. Just like hyaluronic acid, the paste-like substance occurs in your body naturally.
Fat Implants
Your plastic surgeon may harvest tissue from body parts like the abdomen or inner thighs and implant it in your face to fill creased areas.
You deserve clear vision. We can help.
With 135+ locations and over 2.5 million procedures performed, our board-certified eye surgeons deliver results you can trust. Your journey to better vision starts here.
References
- Botox Injections. All About Vision.
- Botox Injections. (February 13, 2019). Mayo Clinic.
- What Causes Crossed Eyes? (November 4, 2016). Healthline.
- Eyelid Twitch. (August 6, 2018). Healthline.
- Botulinum Toxin Injection for the Treatment of Epiphora in Lacrimal Outflow Obstruction. (March 6, 2015). Eye: The Scientific Journal of the Royal College of Ophthalmology.
- Botox: Good for the Eyes, Not Just for Wrinkles. (January 20, 2009). Everyday Health.
- Forehead Botox: The Cost, Benefits, and Everything Else to Know. (July 2019). Harper’s Bazaar.
- Duration of Clinical Efficacy of OnabotulinumtoxinA in Crow’s Feet Lines: Results From Two Multicenter, Randomized, Controlled Trials. (May 2016). Dermatologic Surgery.
- Can You Use Botox Under Your Eyes? (May 2018). Medical News Today.
- How to Make Your Botox Last Longer, According to Dermatologists. (May 2020). Well + Good.
- Injectables & Wrinkle Treatment. American Academy of Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery.
- Botox Cosmetic. (February 2021). DailyMed.
- Botox. (July 2021). DailyMed.
- How Much do Botulinum Toxin Injections Cost? American Society of Plastic Surgeons.
This content is for informational purposes only. It may have been reviewed by a licensed physician, but is not intended to serve as a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult your healthcare provider with any health concerns. For more, read our Privacy Policy and Editorial Policy.